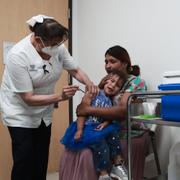
Alla på Scientologfartyget ska mässlingundersökas
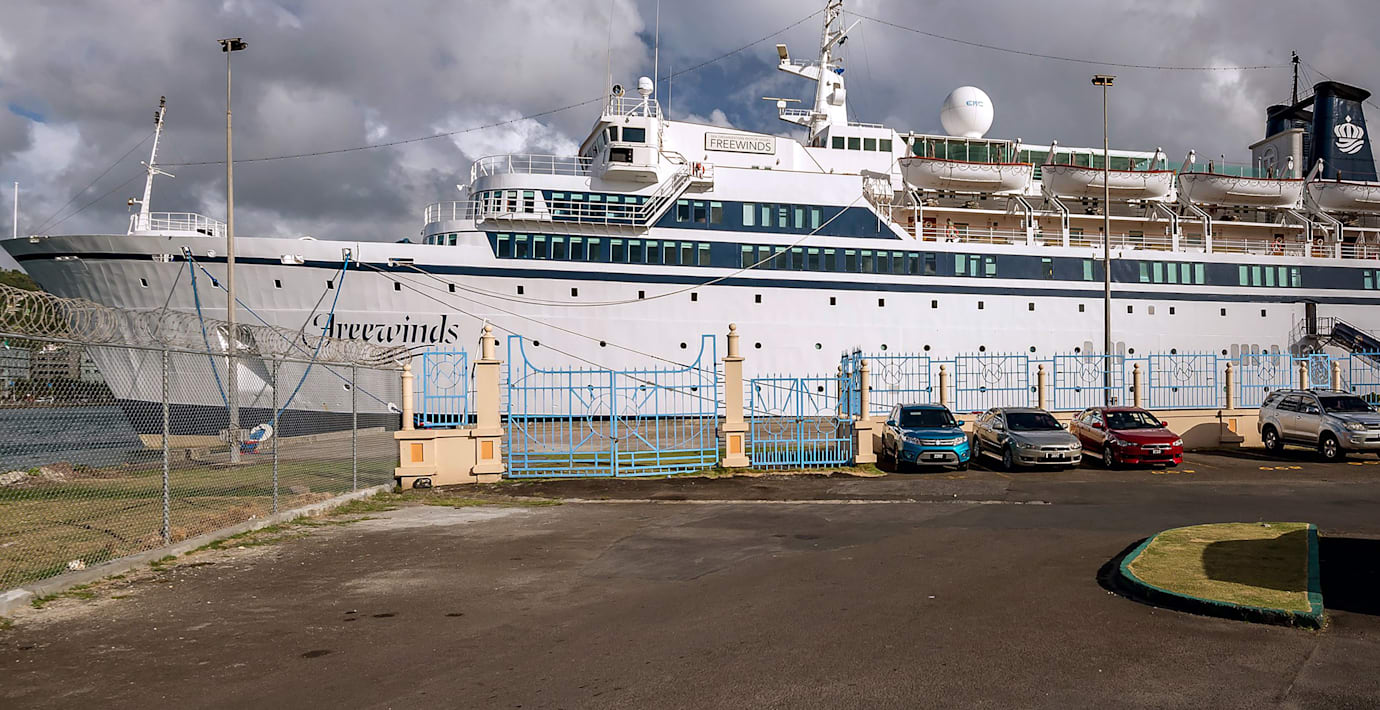
För att undvika spridningen av mässling har myndigheter på ön Curaçao i Västindien beslutat sig för att undersöka passagerarna på kryssningsfartyget Freewinds, som tillhör Scientologikyrkan, innan de får kliva iland på ön, rapporterar Reuters.
Fartyget sattes i karantän i hamnen på ön Saint Lucia efter att en person ombord hade mässling. Efter att 100 doser vaccin levererats till fartyget kunde man i går kväll lämna hamnen och sätta kurs mot Curaçao som är nästa stopp på kryssningen.
Epidemiologen Izzy Gerstenbluth säger att alla passagerare som kan bevisa att de är vaccinerade eller redan har haft den smittsamma sjukdomen kommer att tillåtas att lämna fartyget.
Läs mer
bakgrund
Mässlingen
Wikipedia (en)
Measles is a highly contagious infectious disease caused by the measles virus. Symptoms usually develop 10–12 days after exposure to an infected person and last 7–10 days. Initial symptoms typically include fever, often greater than 40 °C (104 °F), cough, runny nose, and inflamed eyes. Small white spots known as Koplik's spots may form inside the mouth two or three days after the start of symptoms. A red, flat rash which usually starts on the face and then spreads to the rest of the body typically begins three to five days after the start of symptoms. Common complications include postinfection weakening of the immune system and an increased risk of secondary infections leading to diarrhea (in 8% of cases), middle ear infection (7%), and pneumonia (6%). Less commonly seizures, blindness, or inflammation of the brain may occur. Other names include morbilli, rubeola, red measles, and English measles. Both rubella, also known as "German measles", and roseola are different diseases caused by unrelated viruses.Measles is an airborne disease which spreads easily through the coughs and sneezes of infected people. It may also be spread through contact with saliva or nasal secretions. Nine out of ten people who are not immune and share living space with an infected person will be infected. People are infectious to others from four days before to four days after the start of the rash. Most people do not get the disease more than once. Testing for the measles virus in suspected cases is important for public health efforts.The measles vaccine is effective at preventing the disease, and is often delivered in combination with other vaccines. Vaccination resulted in a 75% decrease in deaths from measles between 2000 and 2013, with about 85% of children worldwide being vaccinated as of 2014. Once a person has become infected, no specific treatment is available, although supportive care may improve outcomes. Such care may include oral rehydration solution (slightly sweet and salty fluids), healthy food, and medications to control the fever. Antibiotics may be used if a secondary bacterial infection such as bacterial pneumonia occurs. Vitamin A supplementation is also recommended in the developing world.Measles affects about 20 million people a year, primarily in the developing areas of Africa and Asia. While often regarded as a childhood illness, it can affect people of any age. It is one of the leading vaccine-preventable disease causes of death. In 1980, 2.6 million people died of it, and in 1990, 545,000 died; by 2014, global vaccination programs had reduced the number of deaths from measles to 73,000. Rates of disease and deaths, however, increased in 2017 to 2019 due to a decrease in immunization. The risk of death among those infected is about 0.2%, but may be up to 10% in people with malnutrition. Most of those who die from the infection are less than five years old. Measles is not believed to affect other animals.
Omni är politiskt obundna och oberoende. Vi strävar efter att ge fler perspektiv på nyheterna. Har du frågor eller synpunkter kring vår rapportering? Kontakta redaktionen