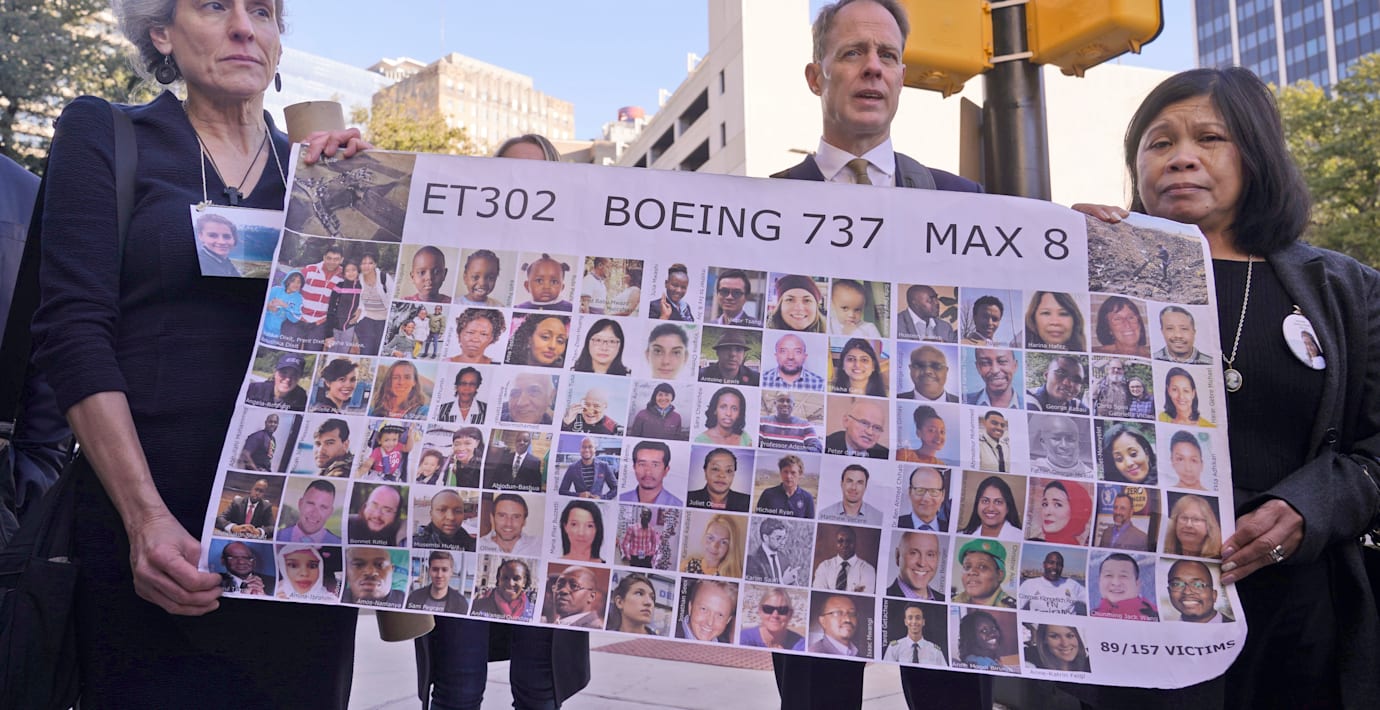
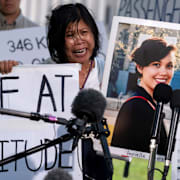Boeing bekräftar uppgörelse efter dödliga 737 Max-olyckor
Flygplanstillverkaren Boeing bekräftar nu den uppgörelse med USA:s justitiedepartement som först rapporterades i maj, rörande bolagets ansvar för de två dödliga 737 Max-krascherna 2018 och 2019. Det framgår av en anmälan till den amerikanska finansmyndigheten SEC, rapporterar BBC.
Uppgörelsen innebär att Boeing ska betala totalt 1,1 miljarder dollar. Av beloppet går 444,5 miljoner till anhöriga, 455 miljoner till förbättrade säkerhets- och kvalitetsrutiner, samt 487,2 miljoner i straffavgifter – varav hälften betalades redan 2021.
Om uppgörelsen godkänns av domstol undviker Boeing ett åtal för bedrägeri. De två olyckorna krävde sammanlagt 346 människoliv.
bakgrund
Boeing 737 Max
Wikipedia (en)
The Boeing 737 MAX is a series of narrow-body aircraft developed by Boeing Commercial Airplanes as the fourth generation of the Boeing 737. It succeeds the Boeing 737 Next Generation and incorporates more efficient CFM International LEAP engines, aerodynamic improvements such as split-tip winglets, and structural modifications. The program was announced in August 2011, the first flight took place in January 2016, and the aircraft was certified by the U.S. Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) in March 2017. The first delivery, a MAX 8, was made to Malindo Air in May 2017.
The 737 MAX series includes four main variants—the MAX 7, MAX 8, MAX 9, and MAX 10—with increasing fuselage length and seating capacity. Boeing also developed a high-density version, the MAX 8-200, launched by Ryanair. The aircraft typically seats 138 to 204 passengers in a two-class configuration and has a range of 3,300 to 3,850 nautical miles [nmi] (6,110 to 7,130 km; 3,800 to 4,430 mi). As of April 2025, Boeing had delivered 1,813 aircraft and held orders for 4,742 more. The MAX 8 is the most widely ordered variant. As of April 2025, the MAX 7 and MAX 10 had not yet received FAA certification, and the agency has not provided a timeline for their approval. Its primary competitor is the Airbus A320neo family, which occupies a similar market segment.
Two fatal accidents, Lion Air Flight 610 in October 2018 and Ethiopian Airlines Flight 302 in March 2019, led to the global grounding of the 737 MAX fleet from March 2019 to November 2020. The crashes were linked to the Maneuvering Characteristics Augmentation System (MCAS), which activated erroneously due to faulty angle of attack sensor data. Investigations revealed that Boeing had not adequately disclosed MCAS to operators and identified shortcomings in the FAA's certification process. The incidents caused significant reputational and financial damage to Boeing, including billions of dollars in legal settlements, fines, and cancelled orders.
Following modifications to the flight control software and revised pilot training protocols, the aircraft was cleared to return to service. By late 2021, most countries had lifted their grounding orders. However, the type came under renewed scrutiny after a January 2024 incident in which a door plug detached mid-flight on Alaska Airlines Flight 1282, causing a rapid decompression. The FAA temporarily grounded affected MAX 9 aircraft, and investigations raised further concerns about production quality and safety practices at Boeing.
Läs mer
Omni är politiskt obundna och oberoende. Vi strävar efter att ge fler perspektiv på nyheterna. Har du frågor eller synpunkter kring vår rapportering? Kontakta redaktionen