Wikipedia (en)
In video game terminology, a loot box (also called a loot crate or prize crate) is a consumable virtual item which can be redeemed to receive a randomised selection of further virtual items, or loot, ranging from simple customisation options for a player's avatar or character to game-changing equipment such as weapons and armour. A loot box is typically a form of monetisation, with players either buying the boxes directly or receiving the boxes during play and later buying "keys" with which to redeem them. These systems may also be known as gacha (based on gashapon, i.e. capsule toys), which is popular in Japan, and may be integrated into gacha games.
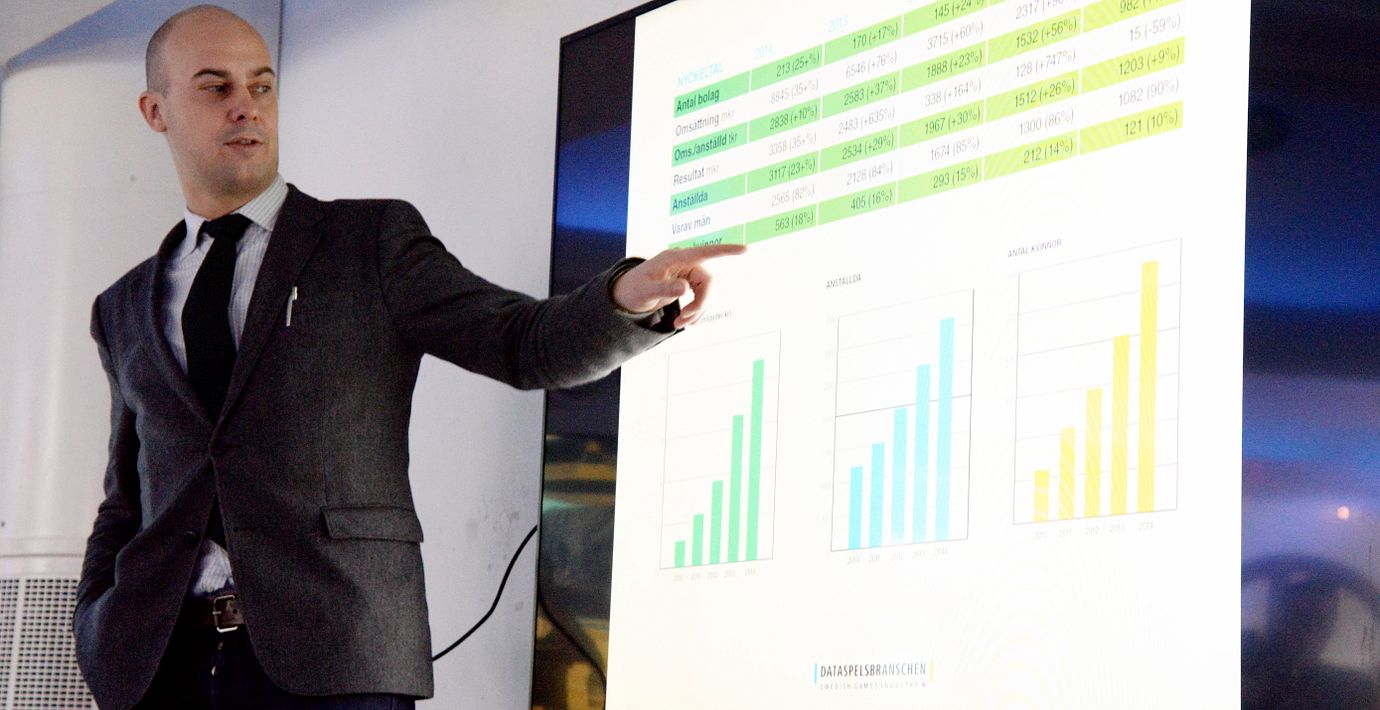
Loot box concepts originated from loot systems in massively multiplayer online role-playing games, and from the monetisation of free-to-play mobile gaming. They first appeared in 2004 through 2007, and have appeared in many free-to-play games and in some full-priced titles since then. They are seen by developers and publishers of video games not only to help generate ongoing revenue for games while avoiding drawbacks of paid downloadable content or game subscriptions, but to also keep player interest within games by offering new content and cosmetics through loot-box reward systems. Loot boxes are just one form of chance-based mechanism used in paid reward systems within some digital games, and research has explored their impact on children, youth and families, and the boundaries between gaming and gambling.
Loot boxes were popularised through their inclusion in several games throughout the mid-2010s. By the latter half of the decade, some games, particularly Star Wars Battlefront II, expanded approaches to the concept that caused them to become highly criticised. Such criticism included "pay to win" gameplay systems that favoured those that spent real money on loot boxes and negative effects on gameplay systems to accommodate them, as well as them being anti-consumer when implemented in full-priced games. Due to fears of them being used as a source in gray-market skin gambling, loot boxes began to become regulated under national gambling laws in various countries at the same time.