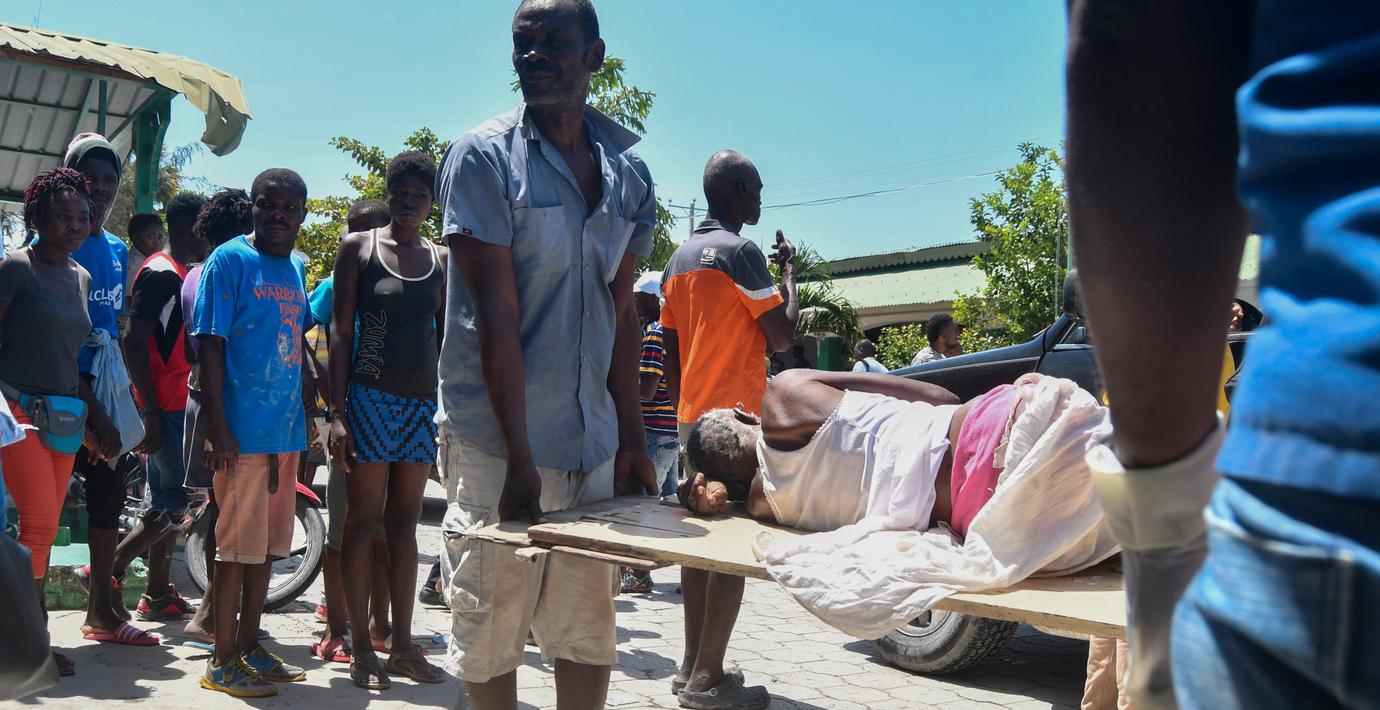
”Salt i såren – Haiti inte redo för en till katastrof”
Haiti är fortfarande kraftigt påverkat av jordbävningen 2010 där hundratusentals människor dog och det politiska kaoset efter mordet på president Jovenel Moïse förra månaden. Det säger Jean Daniel Sénat, journalist på dagstidningen Le Nouvelliste, till Sveriges Radio.
Han kallar lördagens skalv ”salt i såren” för den sargade nationen.
– Haiti är inte redo för ytterligare en katastrof, säger Jean Daniel Sénat.
Landet är ett av världens fattigaste, arbetslösheten är hög och många bor i temporära hus efter skalvet 2010.
Jordbävningen med magnituden 7,2 inträffade i sydvästra Haiti vid 8.30-tiden på lördagsmorgonen, lokal tid. Många människor saknas fortfarande och befaras ligga begravda i rasmassorna. Hittills har minst 304 personer hittats döda.
bakgrund
Jordbävningen som lämnade tusentals döda i landet 2010 hade en magnitud på 7,0
Wikipedia (en)
A catastrophic magnitude 7.0 Mw earthquake struck Haiti at 16:53 local time (21:53 UTC) on Tuesday, 12 January 2010. The epicenter was near the town of Léogâne, Ouest department, approximately 25 kilometres (16 mi) west of Port-au-Prince, Haiti's capital.
By 24 January, at least 52 aftershocks measuring 4.5 or greater had been recorded. An estimated three million people were affected by the quake. Death toll estimates range from 100,000 to about 160,000 to Haitian government figures from 220,000 to 316,000, although these latter figures are a matter of some dispute. The government of Haiti estimated that 250,000 residences and 30,000 commercial buildings had collapsed or were severely damaged. The nation's history of national debt, prejudicial trade policies by other countries, and foreign intervention into national affairs, contributed to the existing poverty and poor housing conditions that increased the death toll from the disaster.The earthquake caused major damage in Port-au-Prince, Jacmel and other cities in the region. Notable landmark buildings were significantly damaged or destroyed, including the Presidential Palace, the National Assembly building, the Port-au-Prince Cathedral, and the main jail. Among those killed were Archbishop of Port-au-Prince Joseph Serge Miot, and opposition leader Micha Gaillard. The headquarters of the United Nations Stabilization Mission in Haiti (MINUSTAH), located in the capital, collapsed, killing many, including the Mission's Chief, Hédi Annabi.Many countries responded to appeals for humanitarian aid, pledging funds and dispatching rescue and medical teams, engineers and support personnel. The most-watched telethon in history aired on 22 January, called "Hope for Haiti Now," raising US$58 million by the next day. Communication systems, air, land, and sea transport facilities, hospitals, and electrical networks had been damaged by the earthquake, which hampered rescue and aid efforts; confusion over who was in charge, air traffic congestion, and problems with prioritising flights further complicated early relief work. Port-au-Prince's morgues were overwhelmed with tens of thousands of bodies. These had to be buried in mass graves.As rescues tailed off, supplies, medical care and sanitation became priorities. Delays in aid distribution led to angry appeals from aid workers and survivors, and looting and sporadic violence were observed. On 22 January, the United Nations noted that the emergency phase of the relief operation was drawing to a close, and on the following day, the Haitian government officially called off the search for survivors.
Saint-Louis-du-Sud
Omni är politiskt obundna och oberoende. Vi strävar efter att ge fler perspektiv på nyheterna. Har du frågor eller synpunkter kring vår rapportering? Kontakta redaktionen